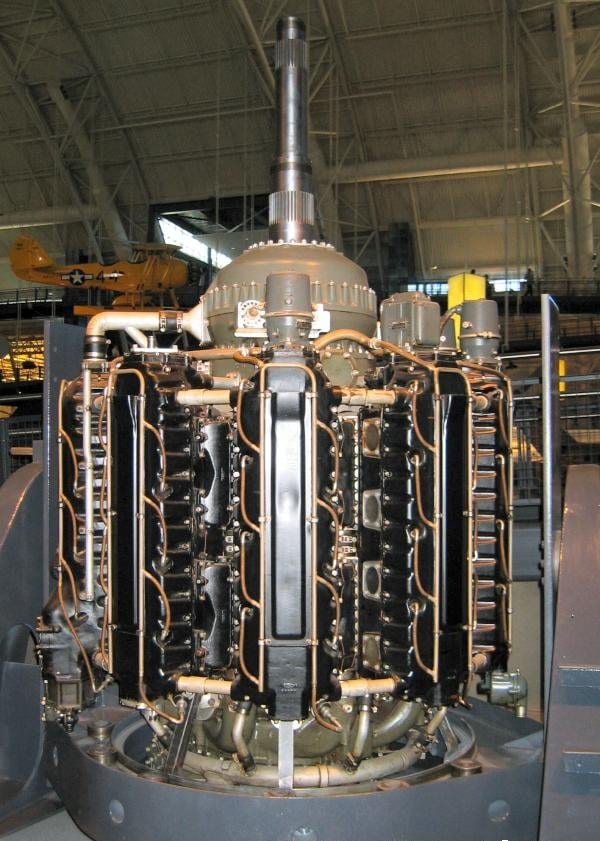
Q: This engine was displayed at this year’s Reno Air Races. There was no information posted at the display, nothing to indicate who owned it, identification/designation, what it was or its intended use. It looked like three P&W R-4360 engines put together. Have you ever seen this engine or might you have any information on it?
It has the appearance of being a real engine yet, none of us in our small group at DVT have been able to find any information on it.
Any thoughts, comments, or information on this engine would be appreciated.
Jim Little

A: Jim, I think you’ve discovered the secret to the next “Unlimited Class” winner at Reno and I suspect the “bookies” are studying the odds already!
Seriously, this has got to be one of the best conversation starters I’ve seen in a long time.
I had my suspicions about this, but I sought outside counsel from a good friend who has attended Reno for many years. Considered the best spark plug analyst, he shares his tremendous knowledge with the race teams.
He confirmed my suspicions and admitted this was just a group of power section parts from several P&W R-4360s. This display “engine” has no crankshaft, accessory case, or magnetos, which would result in making it difficult to get it fired up…and that’s just for starters!
As you may know, Lycoming did, in fact, build a big engine in the mid-1940s designated the XR-7755. It was a 36-cylinder radial with four rows of nine cylinders each. It was liquid cooled and was rated at 5,000 horsepower. It weighed 6,050 pounds dry weight and had a fuel consumption of 580 gph at rated power.
The liquid cooling pump capacity was 750 gpm, which was a common pump capacity of many fire engine pumps.
Supposedly developed for the B-36 bomber, there were three of these engines built and tested by Lycoming. However, none of them ever flew. There is only one of these engines left in captivity and it’s on display at the Smithsonian Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va.
The B-36 ended up using six P&W R-4360 engines and four J-47 jet engines and, as I remember, it made some beautiful noise when it flew overhead.
On a personal note, Jim, I’m proud to tell you that my father was in the engineering group at Lycoming that developed this remarkable engine. It’s amazing to think that this was developed in a very short period of time. There were no computers back then, so the slide rule was the primary resource. I know — what’s a slide rule?
I hope this information has provided all you need to know about the mysterious engine at Reno this year, but I’m positive that what you saw will be the subject of hangar talk for years to come.

A friend of mine has commented as follows: “This looks like a Wright Hyper built from stacks of 7 cylinder radials each with its own crankshaft which was geared to drive 7 output shafts which ran forward between the cylinders to feed into an output gearbox. The 56 cylinder version put out 4000 or so horsepower”.
It is for sure R4360, In flight at about 10,000ft. on C124 I pulled and padded a Generator, Who ever put her together is close to genius. Loved to hear it run. radials for ever.
Merry Christmas.
The X-7755 also had variable cam timing, which was accomplished by having the cylinders in line with a common camshaft. Everything old is new again. Every major automotive breakthrough started with an aviation breakthrough until the mid 90s. Now auto engines have surpassed us.
methinks, this was thrown together as a conversation piece, argument piece, or just a wow factor, by somebody with too much spares and too much time
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qXzYPjNQ6RY
The 28 cylinder PW R-4360 was impressive enough and had the twisted cylinder arrangement in the top picture. It was nick-named the “corncob”. Over 18,000 of them were built. The picture looks like three of them mated together – and while you are probably right there is not a crank in it – there is the reduction gearbox and splined prop shaft just showing far left.
The corncob was notorious if it had a failed cold start and the plugs ended up wet with water from the combustion by-product. Pulling and drying 56 plugs was not for the faint hearted…..